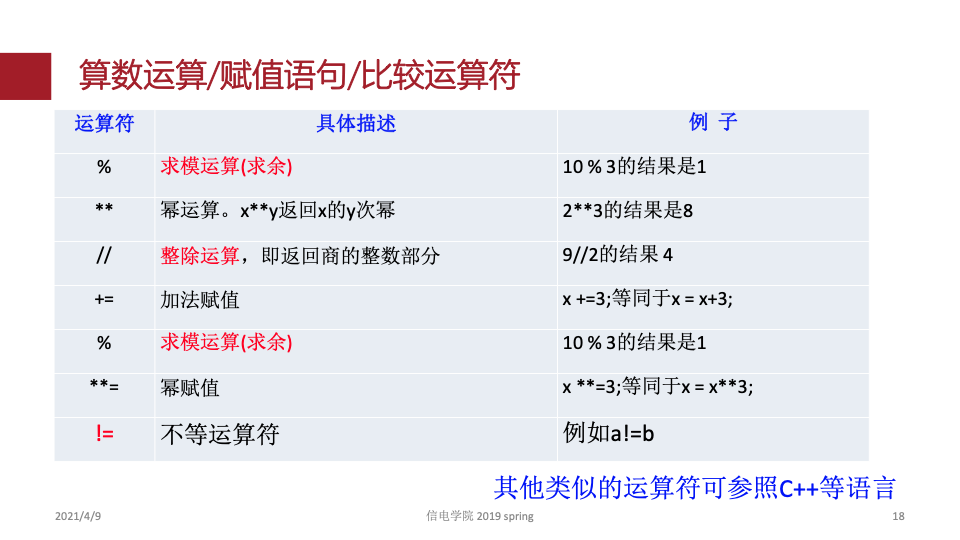
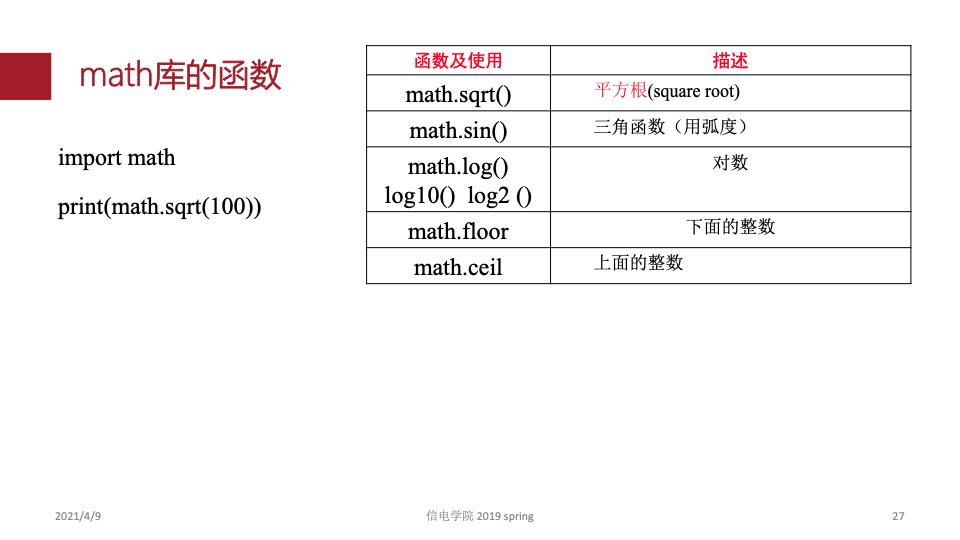
1.python基础
Python还允许用 r“* ” 表示“* ”内部的字符串默认不转义
not 运算为非运算,即把 True 变成 False , False 变成 True 。
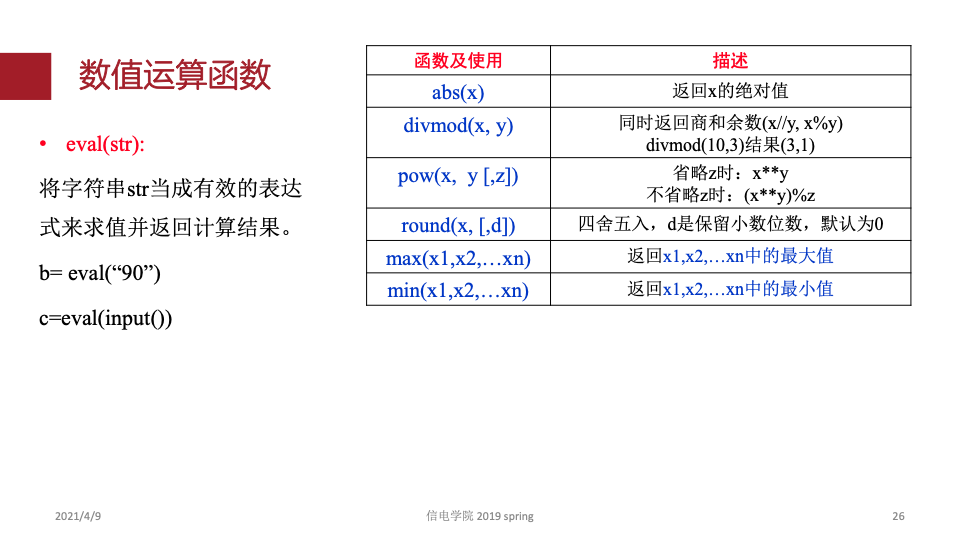
函数 int()、float()、str() 和 bool() 分别用于将变量转换成整型、浮点型、字符串和布尔型变量
除了使用 type() 外,我们还可以使用 isinstance() 来获得数据类型
a = ('apple', 'banana', 'cherry')
b = "Hello World"
c = 55
x = type(a)
y = type(b)
z = type(c)
w=isinstance('2',str)
print(x)
print(y)
print(z)
print(w)
#<class 'tuple'>
#<class 'str'>
#<class 'int'>
#True
注释
#单行
'''
多行
多行
多行
'''
print() print默认最后换行,print(’*‘,end=”)解决问题
Input(‘提示内容’),接受内容默认为str

#摄氏度换成华氏度
A=input('')
aa=eval(A)
F=aa*9/5+32
print(F)
#输入秒数,换算成时分秒并输出,格式:_小时_分钟*秒
A=input('')
aa=eval(A)
H=aa//(1*60*60)
aa=aa-H*60*60
M=aa//60
aa=aa-M*60
S=aa
print(H,M,S)
#将用户输入的一个三位数反转并输出,如 359成953
A=input('')
aa=eval(A)
G=(aa)%10
S=(aa/10)%10
B=(aa/100)%10
G=int(G)
S=int(S)
B=int(B)
Sh=G*100+S*10+B
print(Sh)
2.控制和循环结构

- range(start, stop, step) : start ~ stop – 1,step为步长
- range(100) 0~99 左闭右开
- for 变量 in range(参数) #与for循环结合使用
while 判断条件:
执行语句 #不确定循环次数时用
#程序可以接收用户输入的若干个数并输出其平方根,直到用户输入0退出程序
#程序可以接收用户输入的若干个数并输出其平方根,直到用户输入0退出程序
while True:
a=float( input("请输入一个数") )
if a==0:
break
print( "平方根为:", math.sqrt(a) )
• break:结束整个循环 • continue:结束本次循环,继续下一次的循环
自动出10道题并判分
import random
flang=0
for f in range(1,11):
i=random.randint(1, 10)
j=random.choice('+-*/')
o=random.randint(1, 10)
print('第',f,'题:')
print('')
print(i,j,o,'=',' ','?',end='')
S=input('')
s=eval(S)
if j=='+':
if s==i+o:
print('√')
flang=flang+1
else:
print('x')
elif j=='-':
if s==i-o:
print('√')
flang=flang+1
else:
print('x')
elif j=='*':
if s==i*o:
print('√')
flang=flang+1
else:
print('x')
elif j=='/':
if s==i/o:
print('√')
flang=flang+1
else:
print('x')
print('game over')
print(flang*10)
3.列表、元组、字典、集合
列表list
[value1,vale2] 可重复,可不同类型
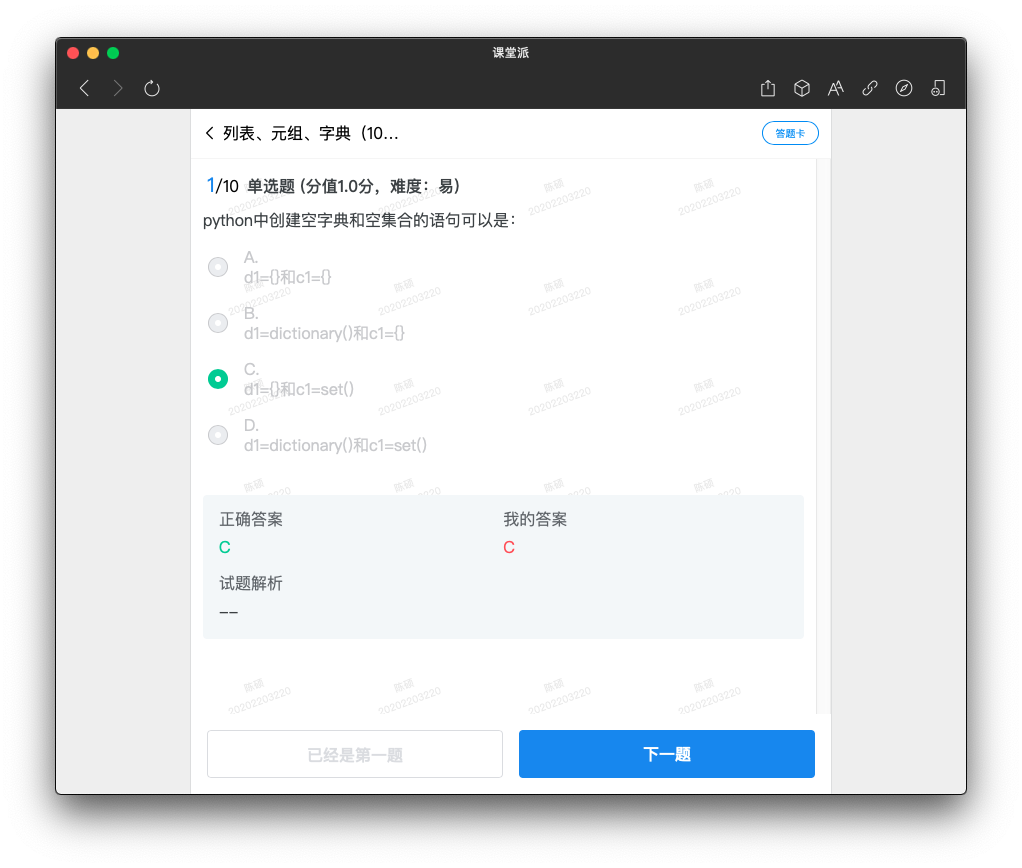
• ls1 = [] 或者 ls1=list() 表示空列表
• 列表可以进行一系列序列操作,如索引、切 片、加、乘和检查成员等
a[0]第一个 a[-1]最后一个
len(a) a列表长度
• 使用append(value)方法添加元素,添加在尾部
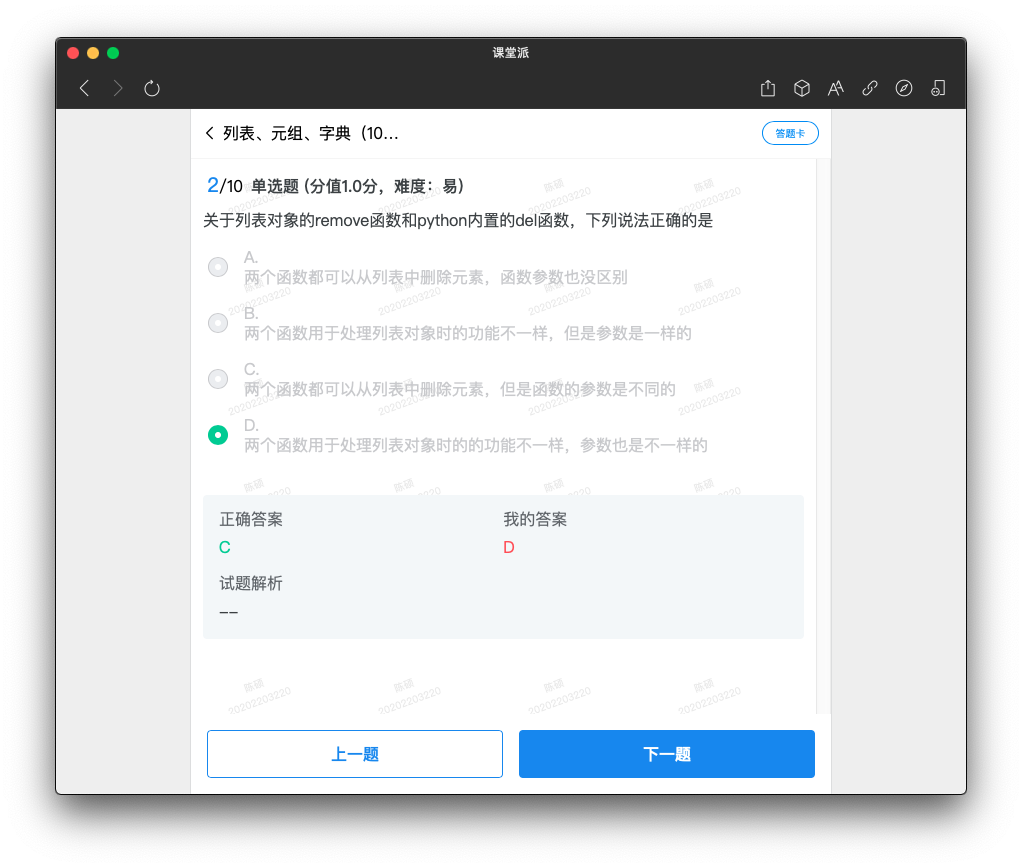
• 使用remove()方法删除元素 remove(value)
#将1-100内所有的奇数保存到列表ls1中
#将1-100内所有的奇数保存到列表ls1中
ls1 = []
for i in range(1,101):
if i%2!=0:
ls1.append(i)
print(ls1)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67, 69, 71, 73, 75, 77, 79, 81, 83, 85, 87, 89, 91, 93, 95, 97, 99]'''
其他删除方法
del函数 del list[index]
pop 函数 list.pop(index)
其他添加方法
insert(index) 指定元素位置「后」添加
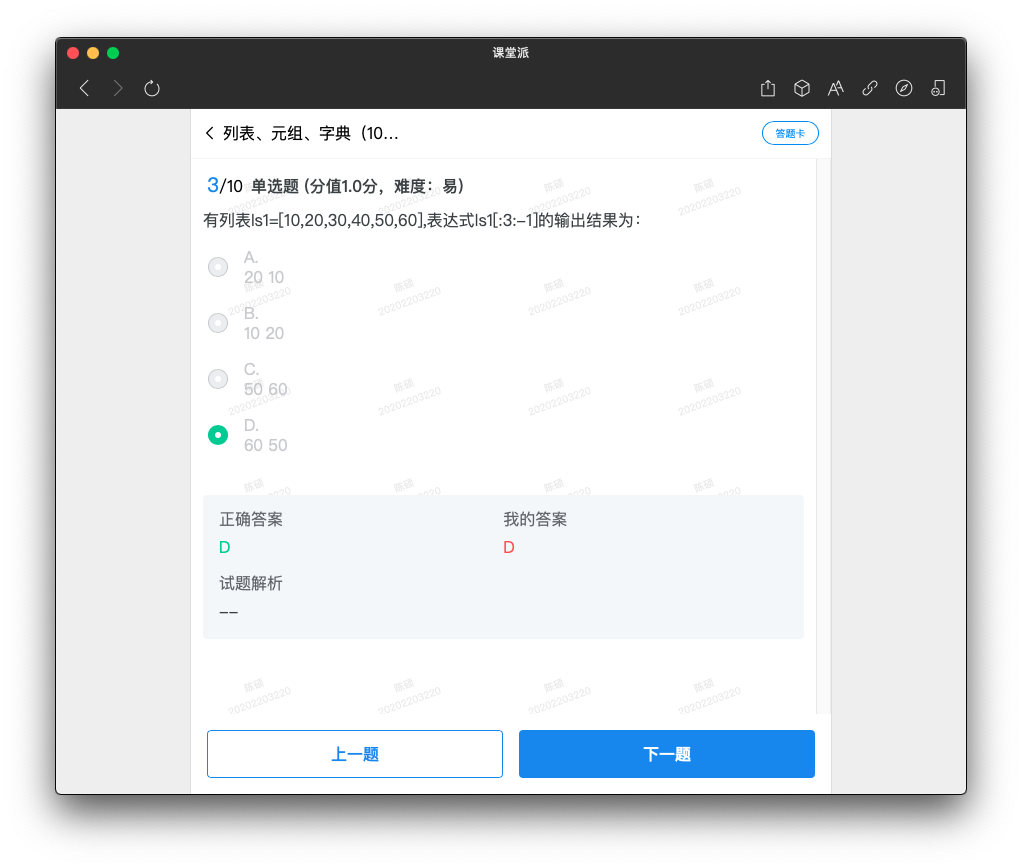
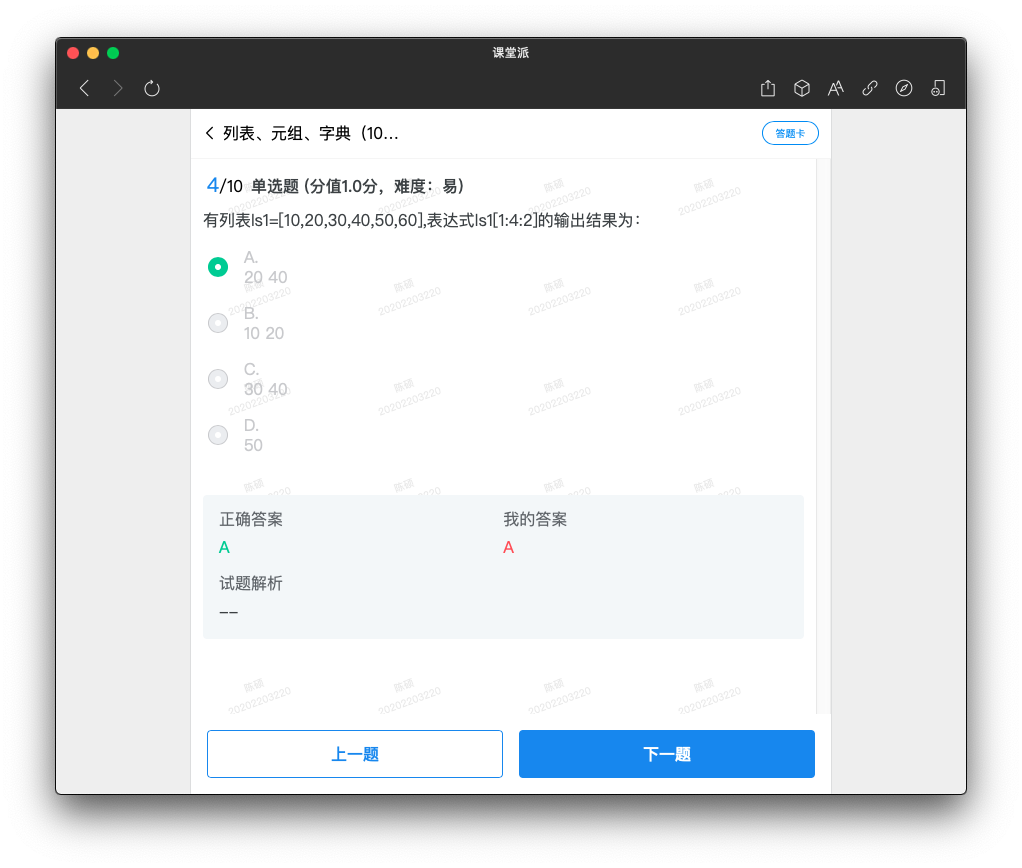
切片
list[start:stop
其他
list.index(value) 返回value值所对应的index
list1.extend(list2) 连接两个列表,list1接list2 ,list1将被改变
• 排序 sorted (a) (a没变,通过返回值保存结果) a.sort() (a排序) • 反序 reversed (a) (a没变,通过返回值保存结果) a.reverse() (a逆序) • 注意sorted()和reversed()函数的返回值类型
ls1=[1,2,3,8,4,5,6,7,8,9,6,10,11]
#计算ls1列表中每个元素的评分,并将结果保存到ls2列表中
ls2 = [ k**2 k in ls1]
#计算ls中所有奇数成员的平方和,结果保存到ls3中
ls3 = [ k**2 for k in ls2 k%2 != 0]
元组tuple
(value1,value2,value3) 可重复,可不同类型
元组对象初始化完成后不可修改
([value1],value2,value3)其中value1为可修改部分 「元组嵌套列表」 >>tuple[0].append(addvale)
a,b=b,a 表示交换两变量
字典dict
{key

#请创建关于科比投篮信息的字典kobe_dict,键为shot_id, 值为shot_zone_area
#请创建关于科比投篮信息的字典kobe_dict,键为shot_id, 值为shot_zone_area
shot_id = [1,2,3] #key
shot_zone_area = ['Right Side(R)','Left Side(L)','Left Side Center(LC)']#value
kobe_dict={} #建立空字典
for key,value in zip(shot_id,shot_zone_area): #for遍历所有的key,value
kobe_dict[key]=value
print(kobe_dict)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
{1: 'Right Side(R)', 2: 'Left Side(L)', 3: 'Left Side Center(LC)'}'''
字典索引
dict[key] / dict.get(key)
kobe_dict = {1: 'Jump Shot', 2:'Jump Shot',3:'Jump Shot', 4:'Jump Shot', 5: 'Driving Dunk Shot', 6: 'Jump Shot', 7: 'Jump Shot'}
kobe_dict[5]
A=kobe_dict.get(1)
B=kobe_dict.get(6)
C=kobe_dict.get(5)
D=kobe_dict.get(-1)
print(A,B,C,D)
print(1 in kobe_dict)#判断是否有此键值
print('Jump Shot' in kobe_dict)#in 不可判断value
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
Jump Shot Jump Shot Driving Dunk Shot None
True
False'''
如果想遍历字典中的键或者值,我们可以使用 keys() 方法或者values()方法
kobe_dict = {1: 'Jump Shot', 2:'Jump Shot',3:'Jump Shot', 4:'Jump Shot', 5: 'Driving Dunk Shot', 6: 'Jump Shot', 7: 'Jump Shot'}
A=kobe_dict.keys()
B=kobe_dict.values()
print(A,B)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
dict_keys([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) dict_values(['Jump Shot', 'Jump Shot', 'Jump Shot', 'Jump Shot', 'Driving Dunk Shot', 'Jump Shot', 'Jump Shot'])'''
取出字典中的键值对
items() 方法,该方法将返回所有键值对,并将其保存在一个元组列表(列表中的元素为元组)
kobe_dict = {1: 'Jump Shot', 2:'Jump Shot',3:'Jump Shot', 4:'Jump Shot', 5: 'Driving Dunk Shot', 6: 'Jump Shot', 7: 'Jump Shot'}
print(kobe_dict.items())
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
dict_items([(1, 'Jump Shot'), (2, 'Jump Shot'), (3, 'Jump Shot'), (4, 'Jump Shot'), (5, 'Driving Dunk Shot'), (6, 'Jump Shot'), (7, 'Jump Shot')])'''
示例
stu ={1:"tom",2:"jack",3:"kitty"}
for k in stu.keys():
print(k,end=' ')
stu={1:"tom",2:"jack",3:"kitty"}
for v in stu.values():
print(v,end=' ')
stu = {1:"tom", 2:"jack",3:"kitty"}
for k, v in stu.items():
print(k,v,end=' ')
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
1 2 3 tom jack kitty 1 tom 2 jack 3 kitty % '''
字典的删减三种方法
– 使用del函数对单一元素或者整个字典进行删除,注意是参数为删除项的key – 使用pop()方法删除单一元素 – 使用clear()方法清空词典的所有元素
kobe_dict = {1: 'Jump Shot', 2:'Jump Shot',3:'Jump Shot', 4:'Jump Shot', 5: 'Driving Dunk Shot', 6: 'Jump Shot', 7: 'Jump Shot'}
del kobe_dict[1]
print (kobe_dict)
kobe_dict.pop(2)
print (kobe_dict)
kobe_dict.clear()
print (kobe_dict)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
{2: 'Jump Shot', 3: 'Jump Shot', 4: 'Jump Shot', 5: 'Driving Dunk Shot', 6: 'Jump Shot', 7: 'Jump Shot'}
{3: 'Jump Shot', 4: 'Jump Shot', 5: 'Driving Dunk Shot', 6: 'Jump Shot', 7: 'Jump Shot'}
{}'''
#统计“there is a beautiful tree.”中各字母出现的次数
message = "there is a beautiful tree."
counts = {}
for char in message:
if char in counts:
counts[char] += 1
else:
counts[char] = 1
print(counts)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
{'t': 3, 'h': 1, 'e': 5, 'r': 2, ' ': 4, 'i': 2, 's': 1, 'a': 2, 'b': 1, 'u': 2, 'f': 1, 'l': 1, '.': 1}'''
message = "there is a beautiful tree."
counts={}
for char in message:
counts [char] = counts.get(char,0)+1
print(counts)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
{'t': 3, 'h': 1, 'e': 5, 'r': 2, ' ': 4, 'i': 2, 's': 1, 'a': 2, 'b': 1, 'u': 2, 'f': 1, 'l': 1, '.': 1}'''
集合set
集合的创建
• 集合的创建有两种方式:使用set()函数或者使用大括号{}
创建空集合,必须使用set(),而不是{},因为{}表示创建一 个空的字典
集合运算

4.文件处理和异常
/
文件读写的一般步骤

1.打开
– f = open(“aaa.txt”, “r“, encoding= “utf-8”)
- 一句话写为 s = open(“xxxx.txt”).read( )
2.读写
– f.read( )、f.readlines()、f.readline()
– f.write(“…”+“\n”)、f.writeline()
3.关闭
– f.close()
文件读取


#读取给定的score.csv中保存的分数信息,按用户输入的学号 或者姓名对学生的信息进行查询和输出
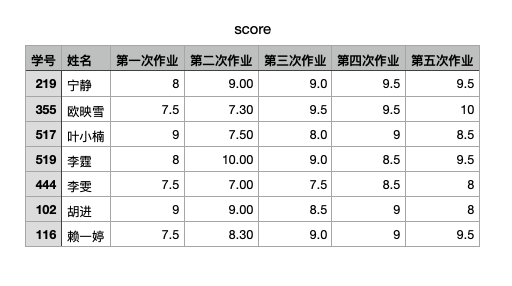
inFile = open("score.csv", "r", encoding="gbk")
key = input("要查找的姓名或学号?")
inFile.readline() #读取并忽略标题行
flag = False
for line in inFile.readlines():
if line == "":
continue #忽略空行
values = line.rstrip('\n').split(",") #注意split的使用
s_id = values[0]
s_name = values[1]
if key in s_id or key in s_name: # 模糊查找
print('学号', s_id, '姓名', s_name)
print("各次成绩:", values[2:])
flag = True
break;
inFile.close()
if not flag:
print('没有找到符合要求的学生记录!')
文件写入
f = open(“aaa.txt”, “==r==“, encoding= “utf-8”) 将‘r’替换为’==w==’
write()逐次写入 writelines()一次性写入
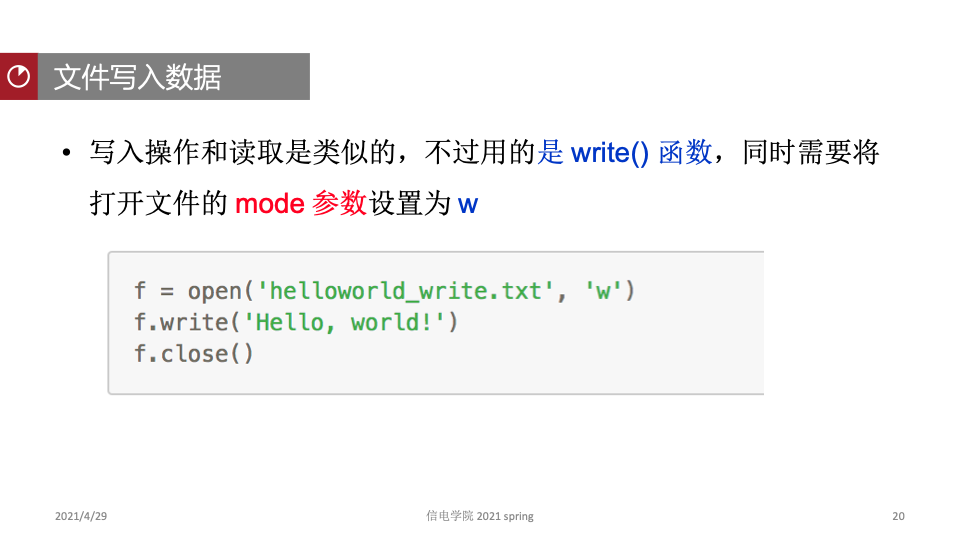
例:

path = 'Pokemon_write.txt '
f= open(path,'w')
#写入Pokemon前两行数据
content = [ ['#', 'Name', 'Type 1', 'Type 2', 'Total','HP', 'Attack', 'Defense', 'Sp. Atk', 'Sp. Def', 'Speed', 'Generation', 'Legendary'],['1', 'Bulbasaur', 'Grass', 'Poison', '318', '45', '49','49','65','65','45','1','FALSE']]
#循环content中内容
for con in content:
con ='\t'.join(con)#是用.join()将列表中每个数值用'\t'联合组成一个字符串
con = con+'\r\n'#每行后添加换行符,如果是linux系统则换成'\n'
f. write(con)
f.close()
其他函数

seek()应用实例

f_obj = open("data.txt", 'r')
f_content0 = f_obj.readline()
f_obj.seek(1,0) #从文件头部偏移1个字节
f_content1 = f_obj.readline()
f_content2 = f_obj.readline()
print(f_content0.strip())
print(f_content1.strip())
print(f_content2.strip())
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP file-seek % python test.py
This is the first line.
his is the first line.
This is the second line.'''
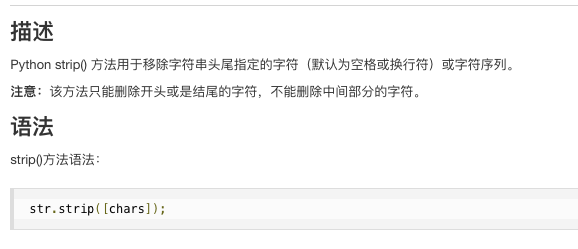
补充:strip()
with

#对于给定的图片sea.jpg,编写程序将文件复制10份,复制的文件命名分别 为sea-copy1.jpg到sea-copy10.jpg
#见实验3.4
os函数

os.sep:取代操作系统特定的路径分隔符
os.name:指示你正在使用的工作平台。比如对于Windows,它是'nt',而对于Linux/Unix用户,它是'posix'。
==os.getcwd:==得到当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径。
os.getenv()和os.putenv:分别用来读取和设置环境变量
os.listdir():返回指定目录下的所有文件和目录名
==os.remove==(file):删除一个文件
os.stat(file):获得文件属性
os.chmod(file):修改文件权限和时间戳
==os.mkdir==(name):创建目录
os.rmdir(name):删除目录
os.removedirs(r“c:\python”):删除多个目录
os.system():运行shell命令
os.exit():终止当前进程
os.linesep:给出当前平台的行终止符。例如,Windows使用'\r\n',Linux使用'\n'而Mac使用'\r' os.path.split():返回一个路径的目录名和文件名 os.path.isfile()和os.path.isdir()分别检验给出的路径是一个目录还是文件 os.path.existe():检验给出的路径是否真的存在 os.listdir(dirname):列出dirname下的目录和文件 os.curdir:返回当前目录(’.‘) os.chdir(dirname):改变工作目录到dirname
os.path.isdir(name):判断name是不是目录,不是目录就返回false os.path.isfile(name):判断name这个文件是否存在,不存在返回false
os.path.exists(name):判断是否存在文件或目录name
os.path.getsize(name):或得文件大小,如果name是目录返回0L
os.path.abspath(name):获得绝对路径
os.path.isabs():判断是否为绝对路径
os.path.normpath(path):规范path字符串形式
os.path.split(name):分割文件名与目录(事实上,如果你完全使用目录,它也会将最后一个目录作为文件名而分离,同时它不会判断文件或目录是否存在)
os.path.splitext():分离文件名和扩展名
os.path.join(path,name):连接目录与文件名或目录
os.path.basename(path):返回文件名
os.path.dirname(path):返回文件路径
#列出文件夹下面的所有文件
import os
listdir = os.listdir()#无参数默认为当前路径#listdir1 =os.listdir(c:\test')
for ls in listdir:
print(ls)
cPath = os.getcwd()
print(cPath)
print('abc.py文件的大小为:{}'.format(os.path.getsize('abc.py')))
例:

import os
path = 'c:\\windows'
dictFile = {}
listdir = os.listdir(path)
for ls in listdir:
if(os.path.isfile(path + '\\' + ls)):
dictFile[ls] = os.path.getsize(path + '\\' + ls)
for k,v in dictFile.items():
if k.split('.')[-1] == 'dll':
print('{}文件的大小为:{}'.format(k,v))
异常



#部分pm25的污染监测数据存储在pollution.txt文件中,数据 格式如下所示读出文件中的数据,计算白天和晚上污染数据的平均值,输 出污染最大的城市的信息
#读取文件中的销售数据信息,计算每个月每种商品的销售总 额和月平均销售额,并以下列各式输出(小数点后保留2位):
f = open('salesdata.txt', 'r')
monthdict = {} #使用一个字典,按月份作为key, 将该月的销售数据的列表作为value
categorydict = {} #使用一个字典,按物品作为key, 将该物品销售数据的列表作为value
for line in f.readlines():
month, category, sales = line.rstrip().split('') #注意一次给多个变量赋值
print(month, category, sales)
if month in monthdict: #如果已存在,则直接追加之
monthdict[month].append(float(sales))
else: #如果该月还不在字典中,则放入一个数据的列表
monthdict[month] = [float(sales)]
if category in categorydict:
categorydict[category].append(float(sales))
else:
categorydict[category] = [float(sales)]
print(categorydict)
#显示统计结果
for month in monthdict:
monthdata = monthdict[month]
print("{}: 销售数据{}, 总额{:.2f}, 平均{:.2f}".format(
month, monthdata, sum(monthdata),
sum(monthdata) / len(monthdata)))
for category in categorydict:
categorydata = categorydict[category]
print("{}物品的销售总额为{:.2f}".format(category, sum(categorydata)))
# 其中:.2f 表示显示格式是:使用小数点后面两位的实数
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP 销售数据分类汇总 % python app_sales_total.py
一月 Games 125.9
十二月 Cars 361.4
一月 Games 450.9
一月 Cars 229.25
一月 Toys 22.5
五月 Games 14.73
一月 Toys 923.1
五月 Cars 675.2
{'Games': [125.9, 450.9, 14.73], 'Cars': [361.4, 229.25, 675.2], 'Toys': [22.5, 923.1]}
一月: 销售数据[125.9, 450.9, 229.25, 22.5, 923.1], 总额1751.65, 平均350.33
十二月: 销售数据[361.4], 总额361.40, 平均361.40
五月: 销售数据[14.73, 675.2], 总额689.93, 平均344.97
Games物品的销售总额为591.53
Cars物品的销售总额为1265.85
Toys物品的销售总额为945.60'''
5.面向对象程序设计
类和对象

创建类
class 类名():
#构建Person类,类有introduce函数成员,函数参数为name,函数体为 输出“大家好,我是***”这样的自我介绍内容。


静态成员
class student():
stuNum = 0
def __init__(self, ag, nam):
self.name = nam
self.age = ag
student.stuNum = student.stuNum + 1
def introduce(self):
print(self.age, self.name, '已建立人数:{}'.format(student.stuNum))
stu1 = student(18,'tom')
stu2 = student(21,'jack')
stu3 = student(23,'kate')
stu1.introduce()
stu2.introduce()
stu3.introduce()
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
18 tom 已建立人数:3
21 jack 已建立人数:3
23 kate 已建立人数:3'''


#实验4.1


@staticmethod 关 键字,默认只能通过类名调用


6.Python中的模块和包
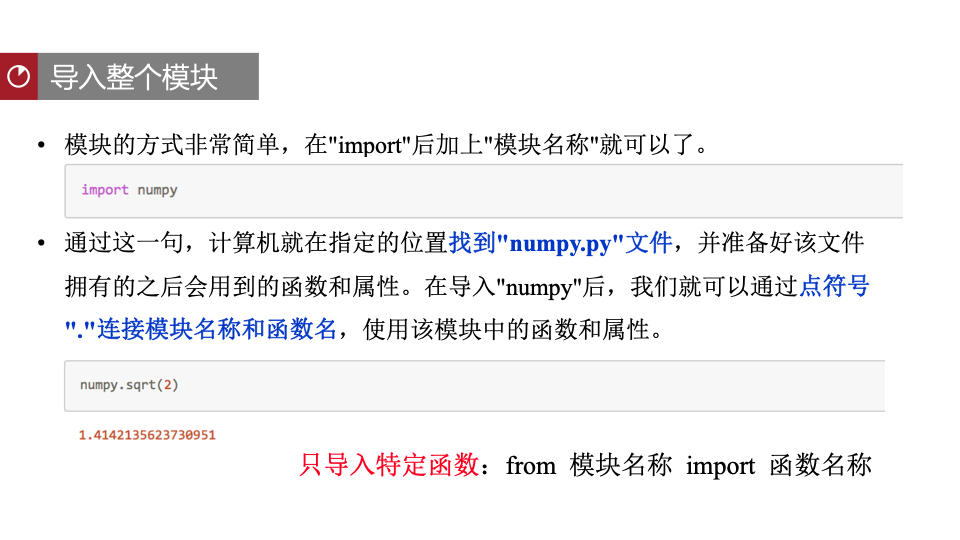
模块install
Cpython:
pin install
Anaconda3:
conda install
模块引入方式
补充:if name == ‘main’:
作用,判断.py是否作为主函数运行,而非模块
jieba词库
安装
pip install 结巴
作用
中文分词,分词结果为列表形式
模式


wordcloud词云
安装:
pip install wordcloud
使用

实例

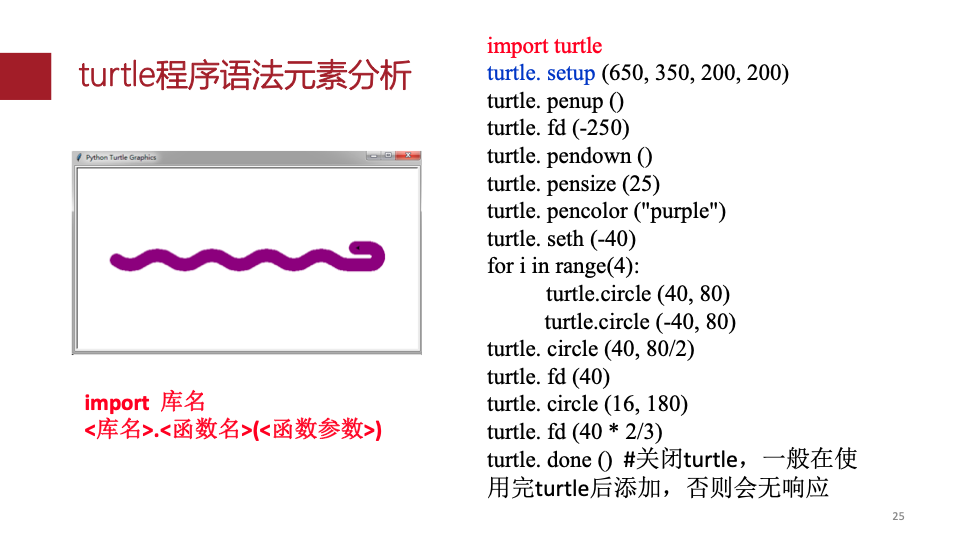
7.Python绘图基础
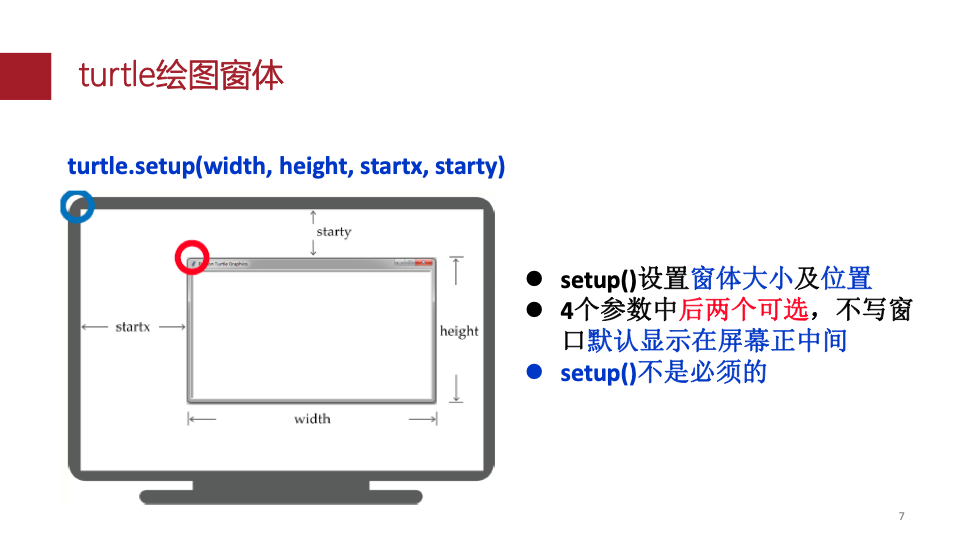
turtle .setup()
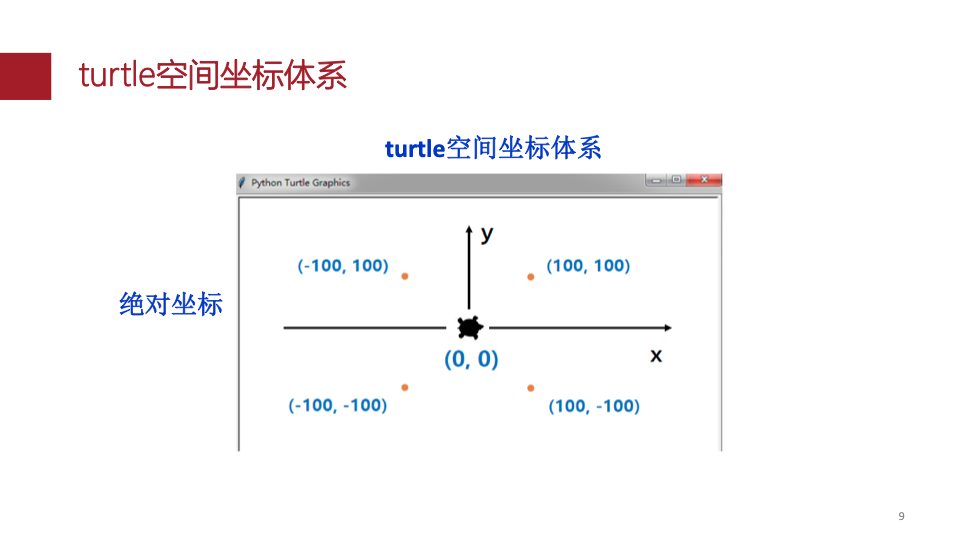
坐标


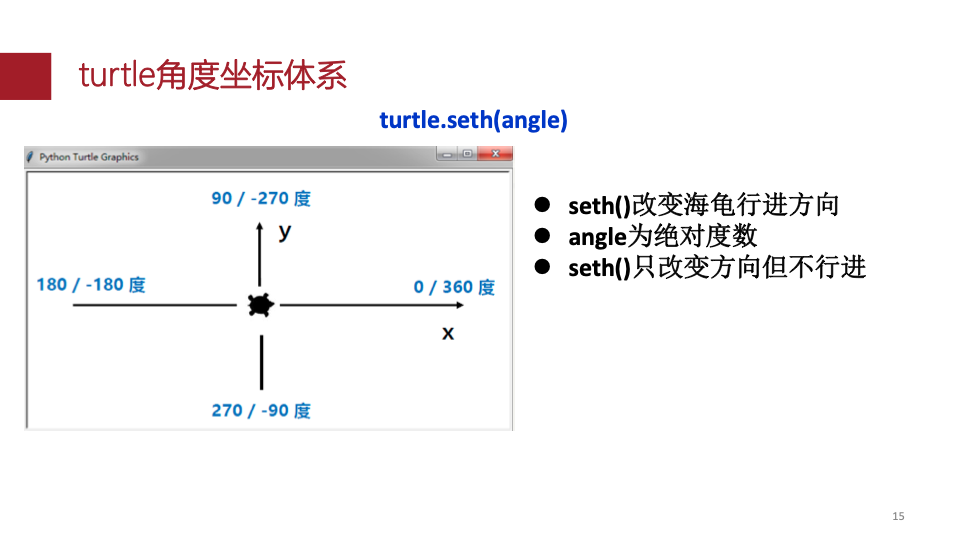
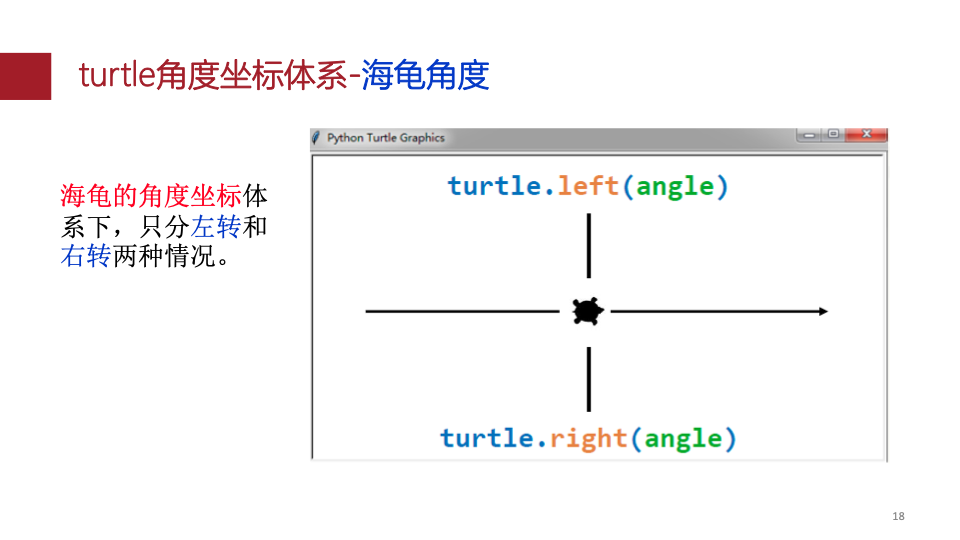
角度

紫色蟒蛇

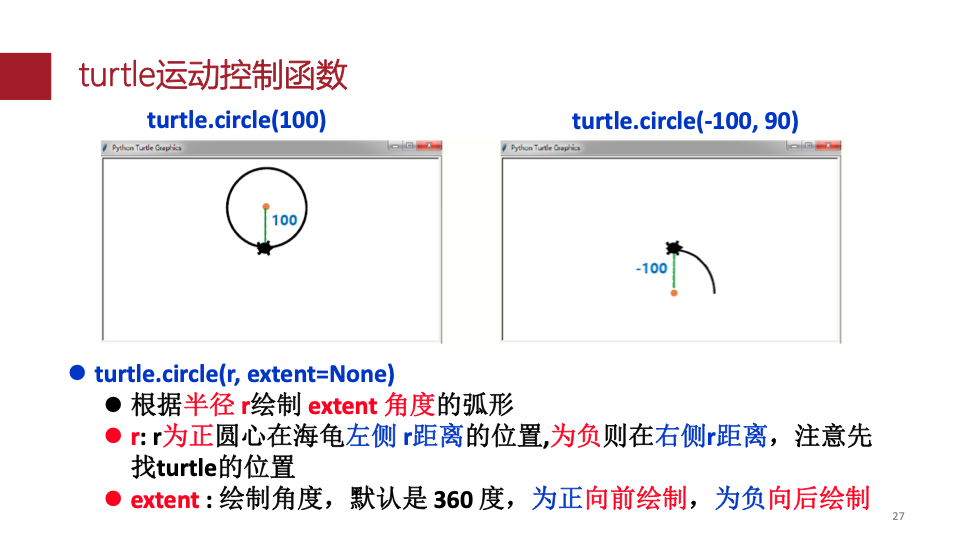
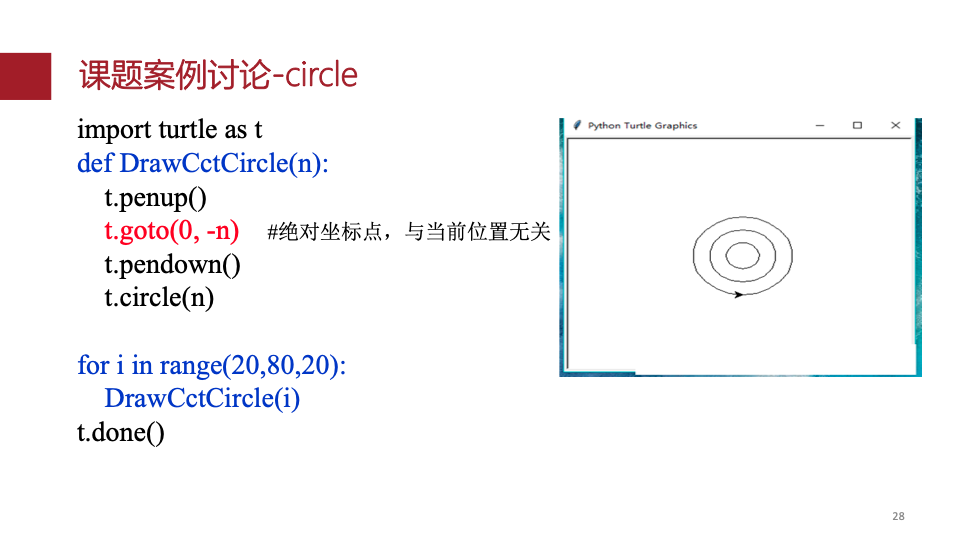
三同心圆


七段数码管

请使用turtle库完成下列图形的绘制:
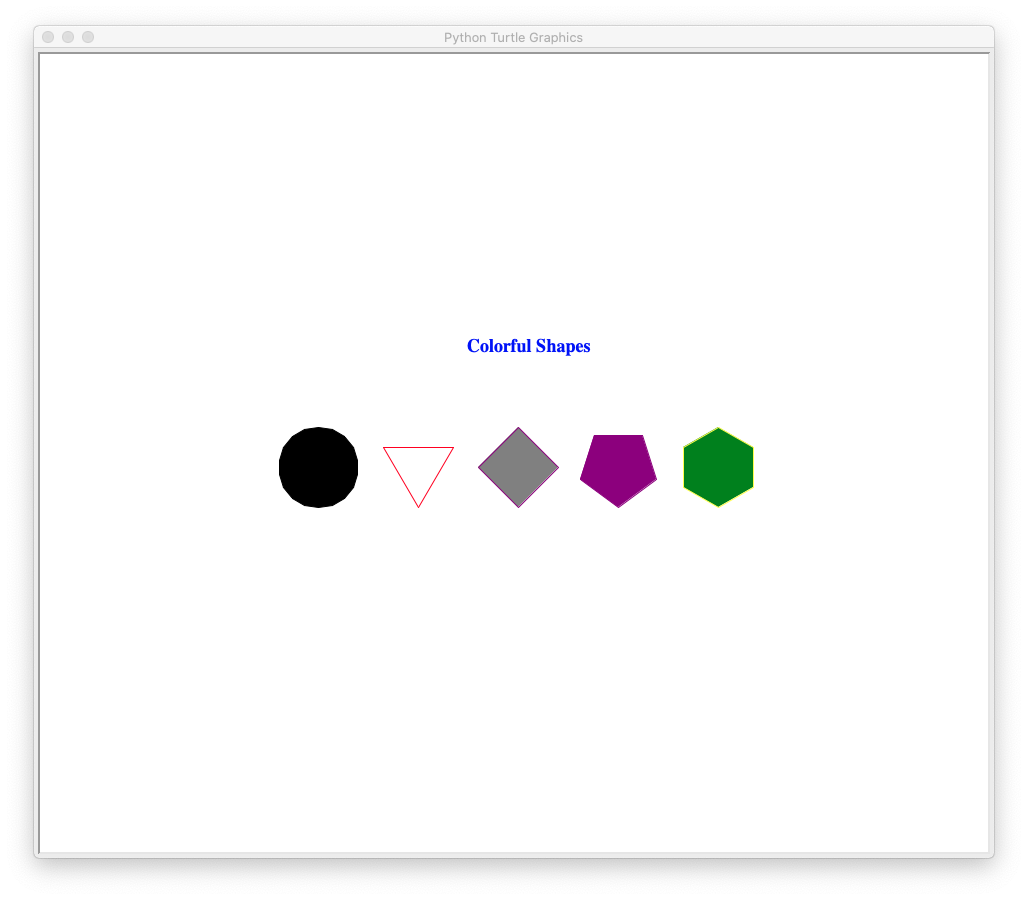
import turtle
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(-200, -50)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.begin_fill() #开始填充
turtle.color("black") #填充黑色
turtle.circle(40)
turtle.end_fill() #填充结束
#turtle.circle(40, steps=3),其中step表示做圆的内切多边形,step=3位3边型
turtle.color("red") #画笔颜色为红色
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(-100, -50)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.circle(40, steps=3)
turtle.color("purple") #画笔颜色为紫色
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(0, -50)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.begin_fill() #开始填充
turtle.fillcolor("gray") #填充灰色
turtle.circle(40, steps=4)
turtle.end_fill() #填充结束
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(100, -50)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.begin_fill() #开始填充
turtle.fillcolor("yellow") #fillcolor为黄色
turtle.color("purple") #color为紫色
turtle.circle(40, steps=5)
turtle.end_fill() #填充结束
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(200, -50)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.begin_fill() #开始填充
turtle.color("yellow") #color为黄色
turtle.fillcolor("green") #fillcolor为绿色
turtle.circle(40, steps=6)
turtle.end_fill() #填充结束
turtle.color("blue")
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(-50, 100)
turtle.pendown()
turtle.write("Colorful Shapes", font = ("Times", 18, "bold"))
#隐藏箭头
turtle.hideturtle()
#暂停界面,使得用户能够看见展示的图形
turtle.done()
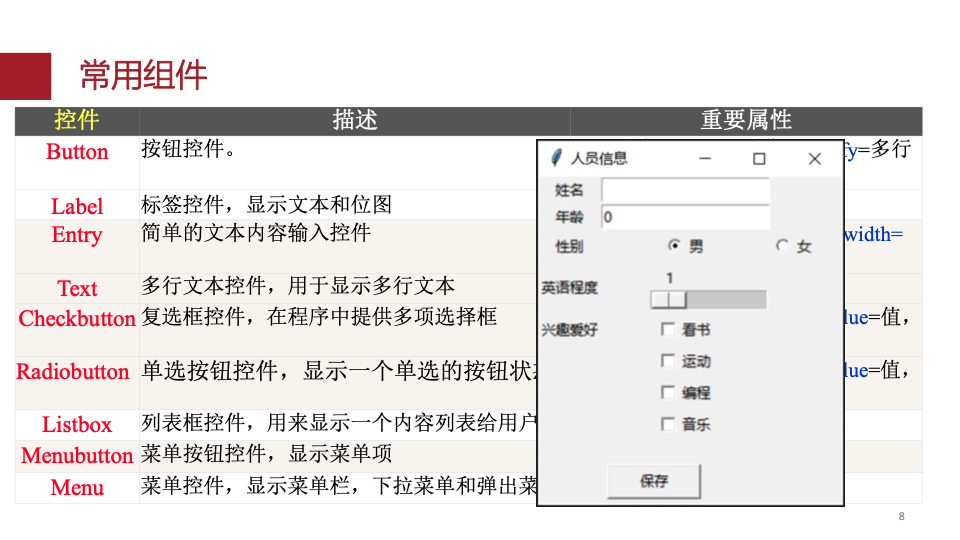
8.图形用户界面
Tkinter
win=Tk() #创建窗口
button = Button(win, text="按钮名称", command=calculate, width=20)#创建单击按钮
button.place(x=100, y=100)#显示创建的组件
win.mainloop()#通过事件循环让窗口循环接收事件




~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
实验1 Python程序控制结构
使用循环结构和range()函数求1-100内所有奇数的和,并输出;
程序解答:
s=0#初始化
z=0
for i in range(101):#0~100
z=z+i
if i%2==0:
s=s+i
print(z-s)#输出打印
接收用户输入的起始整数和终止整数(三位),计算两个整数范围内所有的水仙花数并输出;
程序解答:
a=0
b=0
c=0
i=input('第一个三位数')
o=input('第二个两位数')
I=eval(i)#input输入时为str,eval转化为表达式
O=eval(o)
for I in range(I,O+1):
a = I // 100#//整除 返回整除部分 百位
b = I // 10 % 10#十位
c = I % 10#个位
if a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==I:#各位数^3==I为水仙花数
print(I)
实现进度条程序的设计、实现和调试
import time
j='.' #原理:随for循环借助‘*’改变每个符号数量
q='*'
ap='->'
z=0;
I=0;
O=9;
for i in range(11):
print(z,'%','[',q*I,ap,j*O,']')
z=z+10;
I=I+1
O=O-1
time.sleep(0.7)
import time
for i in range(101):
print("\r{:<3}%".format(i), end="") #end=''保证不换行,\r保证每次回退到行首输出,即覆盖以前的内容
#print("{:3}%".format(i), end="")
time.sleep(0.1)
import time
scale = 10
print("------执行开始------")
for i in range(scale+1):
a = '*' * i
b = '.' * (scale - i)
c = (i/scale)*100
print("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}->{}]".format(c,a,b),end='') #^表示中间对齐,3.0f 三位有效数字小数点后零位
time.sleep(0.2)
print("------执行结束------")
import time
scale=50
print("执行开始".center(scale//2,"-"))
start=time.perf_counter()
for i in range(scale+1):
a='*'*i
b='.'*(scale-i)
c=(i/scale)*100
dur=time.perf_counter()-start
print("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}->{}]已用{:.2f}s".format(c,a,b,dur),end=' ')
time.sleep(0.1)
print("\n"+"执行结束".center(scale//2,'-'))
实验2 列表、元组和字典
#(1)分析并验证下列程序的输出结果,并对结果进行相应的解释。
fibonacci_numbers = [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21] #斐波那契数
aa = fibonacci_numbers
print(aa)
bb = fibonacci_numbers.copy()
print(bb)
fibonacci_numbers.append(9999)
print(fibonacci_numbers)
print(aa)
print(bb)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP 销售数据分类汇总 % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 9999]
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 9999]
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]'''
#(2)给定列表对象students = [‘韩梅梅’, ‘李雷’, ‘林涛’,‘Jim’,‘Kate’,‘Lucy’],验证并给出如下语句的执行结果并进行相应的原因解释。
students = ['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛','Jim','Kate','Lucy']
print(students)
students.append('陈粒')
print(students)
students.append(['陈粒','邵夷贝'])
print(students)
students.extend(['杨洋','张伟'])
print(students)
students.extend('Taylor')
print(students)
students.extend('花粥')
print(students)
students.extend(['谢春花'])
print(students) #append()添加列表形成嵌套列表,extend()会进行拆分
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP 销售数据分类汇总 % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛', 'Jim', 'Kate', 'Lucy']
['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛', 'Jim', 'Kate', 'Lucy', '陈粒']
['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛', 'Jim', 'Kate', 'Lucy', '陈粒', ['陈粒', '邵夷贝']]
['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛', 'Jim', 'Kate', 'Lucy', '陈粒', ['陈粒', '邵夷贝'], '杨洋', '张伟']
['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛', 'Jim', 'Kate', 'Lucy', '陈粒', ['陈粒', '邵夷贝'], '杨洋', '张伟', 'T', 'a', 'y', 'l', 'o', 'r']
['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛', 'Jim', 'Kate', 'Lucy', '陈粒', ['陈粒', '邵夷贝'], '杨洋', '张伟', 'T', 'a', 'y', 'l', 'o', 'r', '花', '粥']
['韩梅梅', '李雷', '林涛', 'Jim', 'Kate', 'Lucy', '陈粒', ['陈粒', '邵夷贝'], '杨洋', '张伟', 'T', 'a', 'y', 'l', 'o', 'r', '花', '粥', '谢春花']'''
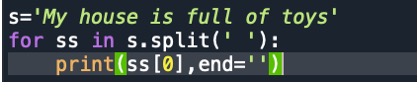
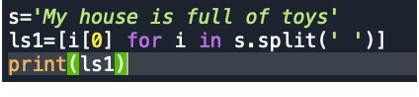
#(3)取出”My house is full of toys”中每个单词的首字母并存储到列表对象中,要求给出两个版本的实现:不使用列表推导式和使用列表推导式。
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP 销售数据分类汇总 % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
Mhifot '''
#(4)已知,以下食物每100g的卡路里如下:
小米粥 45,粗粮馒头 223,全麦面包 235,瘦猪肉 143,鸡翅 194,培根 181,火腿肠 212。
① 立一个空的字典,把上述键值对依此添加进去。通过循环形式,依次显示所有元素,显示格式如“我吃了二两”+“小米粥”,“增加了”+“45”卡路里。
② 计一个“你想知道哪种食物的卡路里?”系统,系统运行时用户可以输入要查询的食物名称,系统显示该食物对应的热量,如果用户输入了不存在的食物,则系统提示“没有该食物的数据!”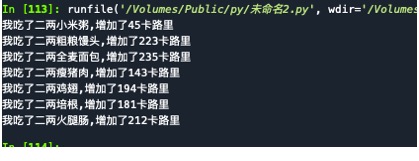
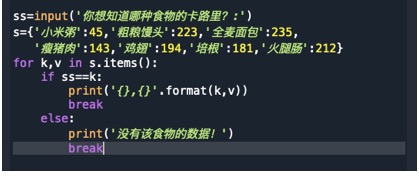
实验3 数据文件操作与异常处理
#(1) 在只打开给定的data.txt文件一次的情况下,实现对文件内容的两次读取:第一次连续读取全部奇数行的数据并输出;第二次连续读取全部偶数行的数据,对数据进行utf-8编码后输出。
l=1
f=open('data.txt','r',encoding='UTF-8')
while True:
s=f.readline()
if not s:
break
else:
if l%2!=0:
print(s)
l+=1
f.seek(0)
l=0
while True:
s=f.readline()
if not s:
break
else:
if l%2!=0:
print(s)
l+=1
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP Desktop % python 未命名0.py
01 this is the first line, jack.
03 this is the third line.
05 this is the fifth line, ab.
02 this is the second line, tom.
04 this is the fourth line, clark.'''
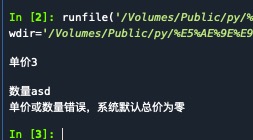
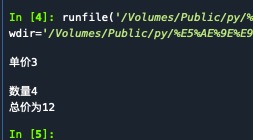
#(2) 编写程序接收用户输入的水果销售单价和数量,计算并输出水果的销售总额。要求程序能够捕获并处理当用户输入非数值类型的单价和数量时系统产生的异常,当捕获到异常时,使用单价和数量的默认值0进行总额的计算,并给用户输出相应的错误提示信息。
try:
price =eval (input('单价'))
number=eval (input('数量'))
print('总价为{}'.format(price*number))
except:
print('单价或数量错误,系统默认总价为零')
#(3) 读取给定的score.txt中保存的分数信息,按用户输入的学号或者姓名对学生的信息进行查询和输出(用户只输入一个查询数据),要求实现模糊条件查询,如姓胡的同学的成绩,学号中包括19字符的同学的成绩?
inFile = open("score.txt", "r", encoding="GBK")
key = input("要查找的姓名或学号?")
inFile.readline() #读取并忽略标题行
for line in inFile.readlines():
if line == "":
continue #忽略空行
values = line.rstrip('\n').split("\t") #注意split的使用
#print(values)
s_id = values[0]
s_name = values[1]
if key in s_id or key in s_name: # 模糊查找
print('学号', s_id, '姓名', s_name)
print("各次成绩:", values[2:])
inFile.close()
#(4).编写程序实现:在实验数据目录中建立子目录copyImg;将实验数据目录中的sea.jpg图片文件拷贝10份到建立的copyImg目录中,文件名依次为seaCopy1.jpg , … , seaCopy10.jpg。
f_obj = open("sea.jpg", 'rb')
import os
path = "/copyImg"
def newfile(path):
path=path.strip()
path=path.rstrip("\\")
# 判断路径是否存在
isExists=os.path.exists(path)
# 不存在
if not isExists:
# 创建目录操作函数
os.makedirs(path)
print(path+' 创建成功')
return True
#存在
else:
print(path+' 目录已存在')
return False
# 定义要创建的目录
newpath="copyImg"
# 调用函数
newfile(newpath)
listdir = os.listdir()
path1=os.getcwd()
f_content = f_obj.read()
os.chdir(path1+path)
for i in range(0,11):
fileName = 'sea-copy' + str(i) + '.jpg'
fnew = open(fileName, 'wb')
fnew.write(f_content)
fnew.close()
print('图片已成功拷贝.')
实验4 数据文件操作与异常处理
#(1)定义point类,具体要求如下:
● 类中数据成员x和y代表点对象的x和y坐标值;
● 类中定义构造函数,实现对x和y的初始化
● 类中定义+运算符重载函数,实现两个点对象相加运算,返回点对象,其x和y坐标分别为参与运算的两个点对象的x坐标和,y坐标和;
● 类中定义点对象(x1,y1)转字符串方法,返回“(x1, y1)”字符串;
● 类中定义*运算符重载函数,实现1个点对象(x1,y1)和整数K的乘法运算,返回点对象,其x和y坐标分别为(kx1, ky1);。
● 设计point类的测试数据,并实现对point类的测试程序。
class Point:
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.__x=x
self.__y=y
def __str__(self):
return "P(%.2f, %.2f)" % (self.__x, self.__y)
def introduce(self):
print('x={},y={}'.format(self.__x, self.__y))
def __add__(self,another):
return Point(self.__x + another.__x, self.__y + another.__y)
def __mul__(self,k):
return Point(self.__x*k, self.__y*k)
P1=Point(10,20)
P2=Point(20,30)
PP0=P1+P2
print("格式输出*2")
P1.introduce()
P2.introduce()
PP1=P1*5
print('加法')
print(PP0)
print('乘法')
print(PP1)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
格式输出*2
x=10,y=20
x=20,y=30
加法
P(30.00, 50.00)
乘法
P(50.00, 100.00)'''
#(2)建立Person类,Student类和Employee类,设计类之间的继承关系,通过实现类来验证类中私有数据成员,子类和父类的继承关系,子类构造函数中调用父类构造函数,以及多态机制等知识点。
class Person():
def __init__(self):
self.name = 'jack'
self.occupation='通訳'
self.day='43'
print('parent class Person init is called')
def introduce(self):
print('hello, my name is {}'.format(self.name))
class Student(Person):
def sayHello(self):
print('Hello, i am the instance of class student,{}'.format(self.name))
class Employee(Person):
def Ehello(self):
print('私は「{}」ともします。{}歳です,{}を担当する,'.format(self.name,self.day,self.occupation))
stu1 = Student()
stu1.introduce()
stu1.sayHello()
stu2 = Employee()
stu2.introduce()
stu2.Ehello()
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
parent class Person init is called
hello, my name is jack
Hello, i am the instance of class student,jack
parent class Person init is called
hello, my name is jack
私は「jack」ともします。43歳です,通訳を担当する,
'''
实验5 python模块
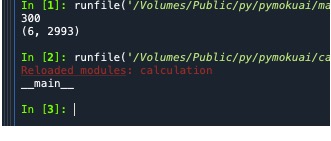
#(1)定义calculation模块(module),具体要求如下:
● 模块中定义Sum1函数,可以计算两个数值的和并返回;
● 模块中定义Mul函数,可以计算两个数值的乘积并返回;
● 在模块中定义CountV函数,可以计算列表或元组数据中的最大和最小值,并返回;
● 在模块中加入print(‘Hello, this is the calculation module.’)程序语句,要求当执行calculation.py文件时,该信息会被输出,当在其他.py文件中以模块形式调用calculation.py文件时,该信息不能被输出;
构建test.py文件,在文件中通过调研calculation模块,实现计算对模块的测试,具体要求如下。
● 建立列表ls1=[10,30,90,94,99,60,80,6,89],通过calculation模块的CountV函数计算最大和最小值,并输出;
● 通过calculation模块的Sum1函数,计算100和 200的和并输出;
● 统计calculation模块的Mul函数,计算100和 200的乘积并输出。
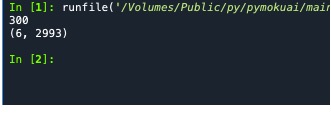
#calculation
import calculation
a=100
b=200
print(calculation.sum1(a,b))
ls1=[10,30,90,94,99,60,80,6,89]
print(calculation.contV(ls1))
def sum1(a,b):
return a+b
def mul(a,b):
return a*b
def contV(p):
minV=19
maxV=2993
for i in p:
if minV>i:
minV=i
if maxV<i:
maxV=i
return minV,maxV
if __name__ =='__main__':
print("__main__")
#(2)通过三国演义文本数据,使用jieba和wordcloud库,基于三国演义中人物的出现频次制作图云对象,要求能够对词云对象中出现的常见问题进行处理(如词云中显示的主要词语不能为非人物名称数据,且同一人物名称不能重复出现)。
import jieba
import wordcloud
excludes = {"将军","却说","荆州","二人","不可","不能","如此","商议","如何",
"主公","军士","左右","军马","引兵","次日","大喜"}
txt = open("/Volumes/Kozakemi/新建文本文档.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8').read()
words = jieba.lcut(txt)
counts = {}
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
elif word == "诸葛亮" or word == "孔明曰":
rword = "孔明"
elif word == "关公" or word == "云长":
rword = "关羽"
elif word == "玄德" or word == "玄德曰":
rword = "刘备"
elif word == "孟德" or word == "丞相":
rword = "曹操"
else:
rword = word
counts[rword] = counts.get(rword,0) + 1
for word in excludes:
del counts[word]
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
cloudlist = []
for i in range(100):
word, count = items[i]
cloudlist.append(word)
new_txt = " ".join(cloudlist)
w = wordcloud.WordCloud(
font_path = "PingFang.ttc",
width = 1000,
height = 700,
background_color = "white",
max_words = 50
)#代表一个文本对应的词云
w.generate(new_txt) #向WordCloud对象w中加载文本
w.to_file("threekingdoms.png")

实验6 图形化用户界面
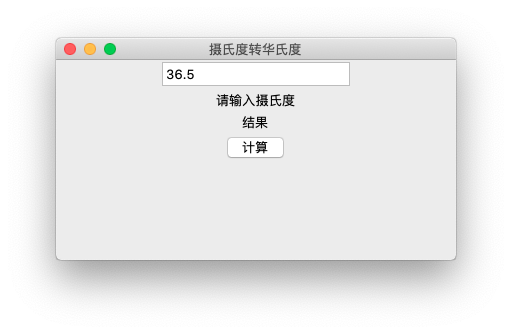
#(1).实现摄氏温度和华氏温度的转换计算,摄氏度转华氏度公式:f = float(c) * 1.8 + 32,具体要求如下
#coding:utf-8
from tkinter import *
win = Tk() #创建窗口
# 变量及事件处理函数
degreeC = StringVar() #与Entry关联的变量
def calculate(): #按钮按下后要执行的函数
c = degreeC.get() # 获取输入框中的值
f = float(c) * 1.8 + 32 # 摄氏度转华氏度
result = f"计算结果:{c}℃ = {f}℉"
label.config(text=result) #显示到标签上
# 窗口
win.title("摄氏度转华氏度") #设置窗口标题
win.geometry("400x220") #设置窗口大小,注意用字母x
# 输入框
entry = Entry(win, textvariable=degreeC, width=20) #创建输入框组件
entry.place(x=100, y=50) #显示Entry组件
# 按钮
button = Button(win, text="进行转换", command=calculate, width=20) #创建按钮组件
button.place(x=100, y=100) #显示按钮组件
# 标签
label = Label(win, text="计算结果", width=20) #创建按钮组件
label.place(x=100, y=150) #显示标签组件
# 初始化变量
degreeC.set('37.5') # 设置变量的初始值
# 显示主窗口
win.mainloop()
#coding:utf-8
#from tkinter import *
import tkinter
win = tkinter.Tk() #创建窗口
# 变量及事件处理函数
degreeC = tkinter.StringVar() #与Entry关联的变量
def calculate(): #按钮按下后要执行的函数
c = degreeC.get() # 获取输入框中的值
f = float(c) * 1.8 + 32 # 摄氏度转华氏度
result = f"计算结果:{c}℃ = {f}℉"
label.config(text=result) #显示到标签上
# 窗口
win.title("摄氏度转华氏度") #设置窗口标题
win.geometry("400x220") #设置窗口大小,注意用字母x
# 输入框
entry = tkinter.Entry(win, textvariable=degreeC, width=20) #创建输入框组件
entry.place(x=100, y=50) #显示Entry组件
# 按钮
button = tkinter.Button(win, text="进行转换", command=calculate, width=20) #创建按钮组件
button.place(x=100, y=100) #显示按钮组件
# 标签
label = tkinter.Label(win, text="计算结果", width=20) #创建按钮组件
label.place(x=100, y=150) #显示标签组件
# 初始化变量
degreeC.set('37.5') # 设置变量的初始值
# 显示主窗口
win.mainloop()
import tkinter #tkinter库,用于图形界面
win =tkinter.Tk() #此句必须写在前面,创建窗口
tempEnt=tkinter.StringVar()#接受输入
def cc(): #Button引用命令
#t1=
c=tempEnt.get()
#c=30
f=float(c)*1.8+32
tt=f"结果{f}"
label.config(text=tt)
win.title('摄氏度转华氏度')
win.geometry("400x200")
ent1=tkinter.Entry(win,textvariable=tempEnt,width=20)
ent1.pack()
lbll=tkinter.Label(text="请输入摄氏度")
lbll.pack()
label=tkinter.Label(text='结果')
label.pack()
btn1=tkinter.Button(text="计算",command=cc)
btn1.pack()
tempEnt.set('36.5')
win.mainloop()
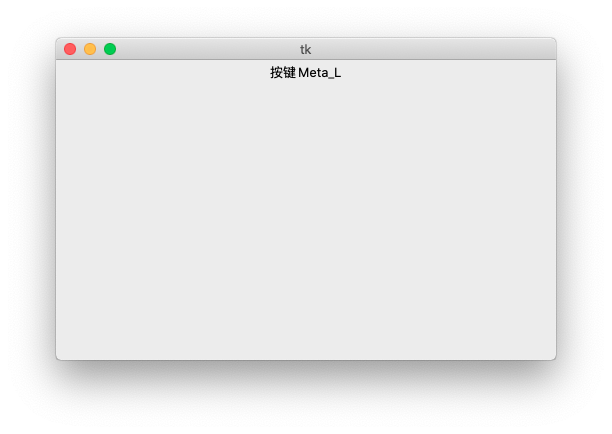
#(2)构建窗体,在窗体上建立Label组件,实现:
l 在Label组件上显示鼠标在窗体上的操作信息,如移动,单击和当前位置信息等,移动时要求显示当前鼠标指针的坐标。
l 当用户按下键盘上的a-z,0-9这些键时,能够在Label组件上显示用户的操作的键。
import tkinter
win = tkinter.Tk()
win.geometry('500x300')
#事件处理函数
def mouse_pressed(event):
label1.config(text=f'鼠标按下:{event.num}')
def mouse_moved(event):
label1.config(text=f'鼠标移动:{event.x},{event.y}')
def key_pressed(event):
label1.config(text='按键:' + event.keysym)
if __name__ == '__main__':
label1 = tkinter.Label(win, width=30)
label1.pack()
#绑定事件
win.bind('<Button>', mouse_pressed)
win.bind('<Motion>', mouse_moved)
win.bind('<Key>', key_pressed)
win.mainloop()
import tkinter
win =tkinter.Tk()
win.geometry('500x300')
def mouse_moved(event):
lbll.config(text='x={},y={}'.format(event.x,event.y))
def mouse_pressed(event):
lbll.config(text='按下{}'.format(event.num))
def key_pressed(event):
lbll.config(text='按键'+event.keysym)
win.bind('<Motion>', mouse_moved)
win.bind('<Button>',mouse_pressed)
win.bind('<Key>', key_pressed)
lbll=tkinter.Label()
lbll.pack()
win.mainloop()
实验7 网络爬虫和正则表达式
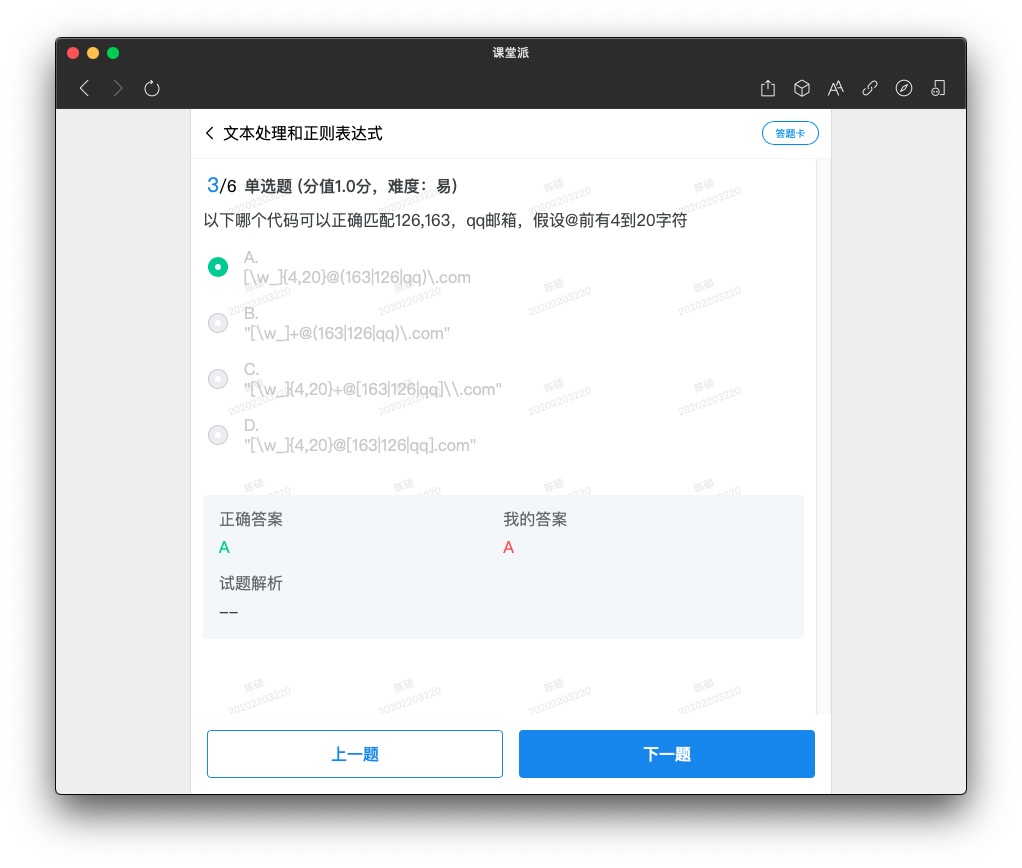
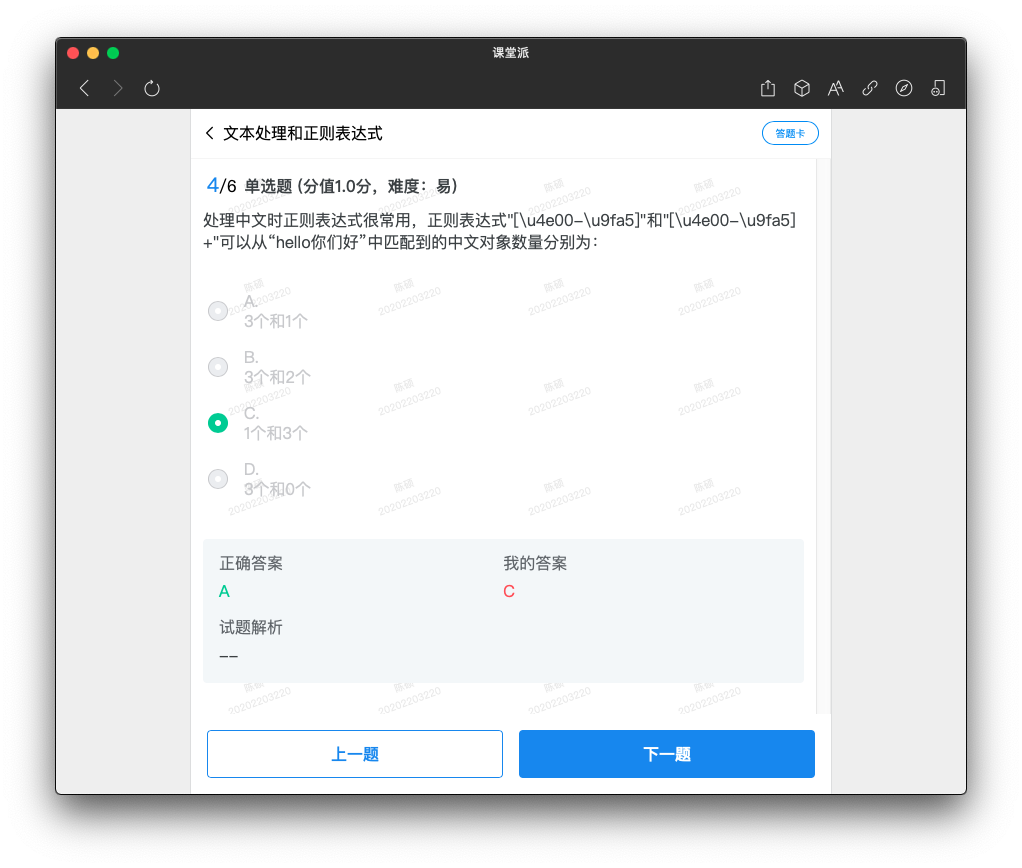
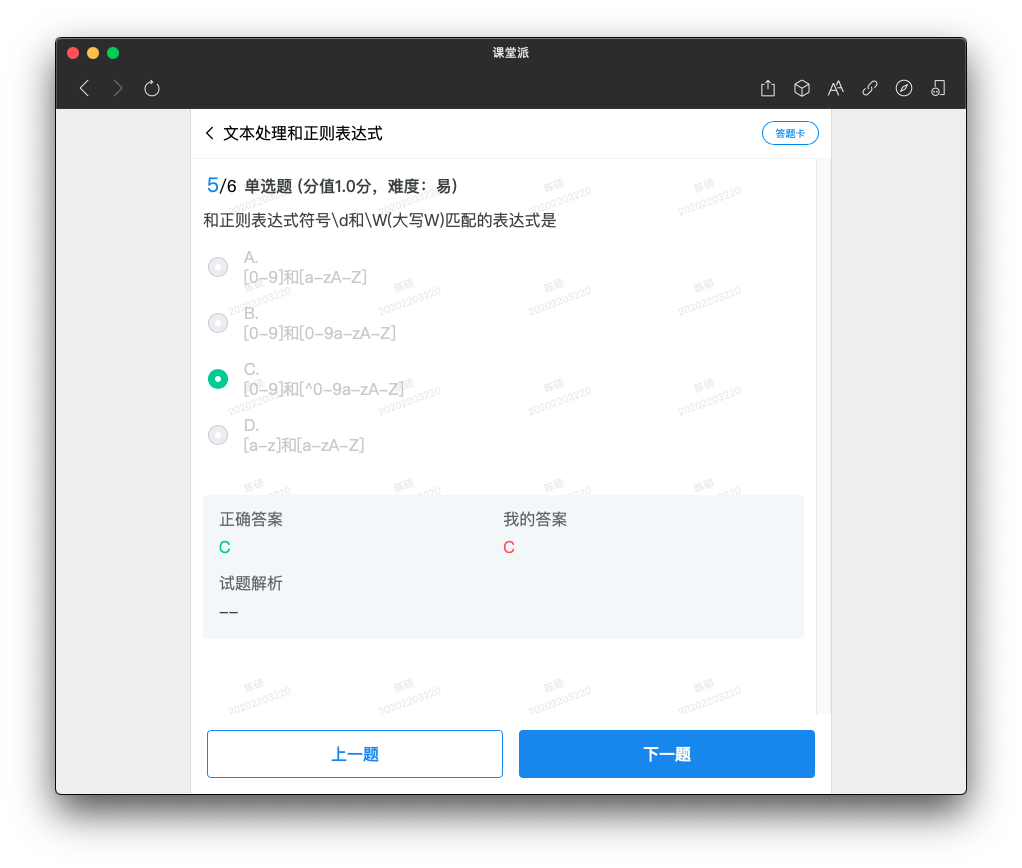
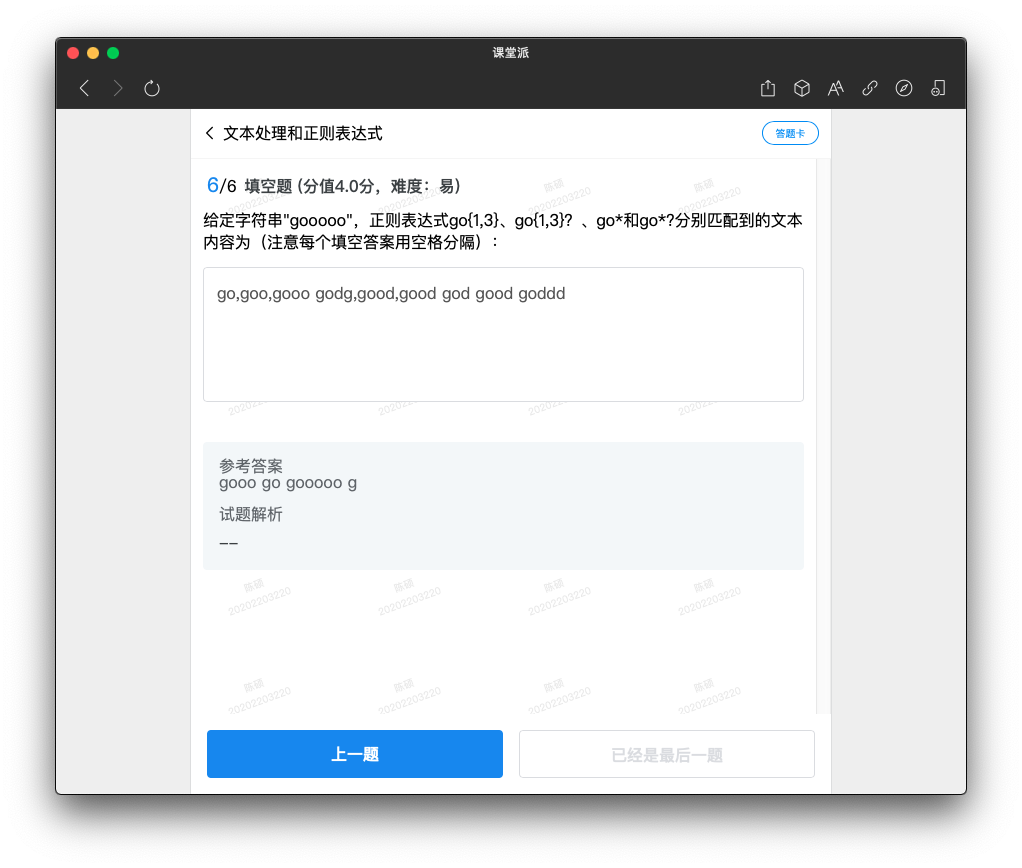
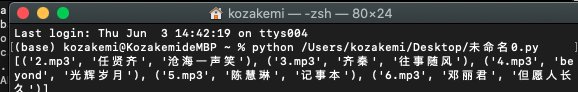
#(1)给定字符串数据 请从其中提取出所有歌曲的演唱者、歌名和链接的歌曲文件名数据,并进行输出。
import re
s = '''<div id="songs-list">
<h2 class="title">经典老歌</h2>
<p class="introduction">经典老歌列表</p>
<ul id="list" class="list-group">
<li data-view="7"><a href="/2.mp3" singer="任贤齐">沧海一声笑</a></li>
<li data-view="41"><a href="/3.mp3" singer="齐秦">往事随风</a></li>
<li data-view="366"><a href="/4.mp3" singer="beyond">光辉岁月</a></li>
<li data-view="5ab"><a href="/5.mp3" singer="陈慧琳">记事本</a></li>
<li data-view="5"><a href="/6.mp3" singer="邓丽君">但愿人长久</a></li>
</ul> </div>'''
p='<li data-view="\w{1,3}"><a href="/(.*)" singer="(.*)">(.*)</a></li>'
ss=re.findall(p,s)
print(ss)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
[('2.mp3', '任贤齐', '沧海一声笑'), ('3.mp3', '齐秦', '往事随风'), ('4.mp3', 'beyond', '光辉岁月'), ('5.mp3', '陈慧琳', '记事本'), ('6.mp3', '邓丽君', '但愿人长久')]'''
#(2)为了分析客户对屏幕的评论数据,需对数据进行标准化处理,如把多个同义词替换为同一个词。请将下列评论数据中的“触摸屏”和“显示屏”替换为“屏幕”:“广告说这个触摸屏很好,推销的人也说屏幕好,但我觉得这个显示屏糟透了”。
import re
ss="广告说这个触摸屏很好,推销的人也说屏幕好,但我觉得这个显示屏糟透了"
S=re.sub('触摸屏屏幕','显示屏',ss)
print(S)
'''(base) kozakemi@KozakemideMBP ~ % python /Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py
广告说这个显示屏很好,推销的人也说显示屏好,但我觉得这个显示屏糟透了'''
#(3)给定新闻网页url为“http://news.qut.edu.cn/zhxw/26.htm”,请从其中提取出所有的新闻标题和发布时间数据,并将结果写入到newsData.txt文件中,其中每行存储一条新闻数据,每条新闻的标题数据和发布时间数据使用空格进行间隔。参照结果如下:
import requests
import re
url='http://news.qut.edu.cn/zhxw/26.htm'
r=requests.get(url)
r.encoding=r.apparent_encoding
#print(r.text)
p='<li id="line_[\S]*" style="display:none;"><a href="..[\S]*" style="float:left;">(.*)</a><span>(.*)</span></li>'
s=re.findall(p,r.text)
print(s)
runfile('/Users/kozakemi/Desktop/未命名0.py', wdir='/Users/kozakemi/Desktop')
[('莘莘学子忙早读 朗朗书声遍理工', '2007-04-26'), ('土木工程学院召开宣传及网络管理工作会议', '2007-04-26'), ('人文学院举办第二届青年教师讲课大赛', '2007-04-26'), ('建筑学院召开素质拓展工作报告交流会', '2007-04-26'), ('土木学院举办双语教学研讨会', '2007-04-25'), ('人文社科学院学生赴中国石油大学进行交流', '2007-04-25'), ('机械学院全力以赴开展评建工作', '2007-04-25'), ('自动化工程学院加强政治理论学习', '2007-04-25'), ('管理学院“五大行动”推进迎评工作', '2007-04-25'), ('机械学院篮球赛落幕', '2007-04-25'), ('机械工程学院入党积极分子监督岗正式启动', '2007-04-24'), ('机械学院举办考研交流会', '2007-04-24'), ('汽车与交通学院强调“迎评创优”学生工作方案', '2007-04-24'), ('商学院举行留学归国教师专题报告会', '2007-04-24'), ('计算机学院赴青岛大学学习评建经验', '2007-04-23'), ('一汽集团向汽车学院赠送汽车模型', '2007-04-23'), ('土木学院学生党员赴团岛灯塔宣誓', '2007-04-23'), ('管理学院:“九个一”工程促迎评', '2007-04-23'), ('人文社科学院举办研究生考试试卷评析报告会', '2007-04-23'), ('通信学院开展青年教师讲课竞赛评比活动', '2007-04-20'), ('通信与电子工程学院重视年青教师培养工作', '2007-04-19'), ('管理学院应邀访问海尔', '2007-04-19'), ('学校召开学生信息员会议', '2007-04-18'), ('环境学院举办公务员考试学习经验交流会', '2007-04-18'), ('通信学院开展学风建设专项检查整改活动', '2007-04-17'), ('经贸学院成立我校首个大学生奥运文化协会', '2007-04-17'), ('通信学院积极推进优良学风班建设', '2007-04-17'), ('土木学院举办远离网瘾心理咨询讲座', '2007-04-17'), ('经贸学院拉开“宿舍文化节”活动序幕', '2007-04-17'), ('建筑学院邀请美国注册建筑师做讲座', '2007-04-17'), ('经贸学院举办四级听力、口语突破讲座', '2007-04-17'), ('建筑学院与琴岛学院联合举办大型学生作品展', '2007-04-17'), ('理学院举办青年教师教学培训班', '2007-04-17'), ('管理学院营造“人人关心评估”的良好氛围', '2007-04-17'), ('商学院全方位开展主题教育活动', '2007-04-16'), ('管理学院加强大学生涯规划教育', '2007-04-16'), ('建筑学院举办美国建筑教育专题讲座', '2007-04-16'), ('机械学院开展师德师风专题学习', '2007-04-12'), ('经贸学院开办视频党课', '2007-04-12')]
其他程序
百钱买百鸡
money = 100
score = 0
for g in range(1,21):
for m in range(1,34):
for x in range(1,301):
score = g*5 + m*3 + float(x)/3
if score == money and g+m+x ==100:
print ('公鸡 %s 只,母鸡 %s 只,小鸡 %s 只' % (g,m,x))
else:
pass
365_1percent
print((1 + 0.01)**365)
print((1 - 0.01)**365)
斜边长度
import math
a = float(input("请输入一条直边"))
b = float(input("请输入另一条直边"))
c = math.sqrt(a*a + b*b)
print("斜边为", c)
词频统计
import jieba
txt = open('/Volumes/Public/py/新建文本文档.txt','r',encoding="utf-8").read()
words = jieba.lcut(txt)
counts={}
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
else:
counts[word]=counts.get(word,0)+1
items=list(counts.items())
items.sort(key = lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
for i in range(15):
word,count = items[i]
print("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word,count))
三国词频+排除
import jieba
path = '/Volumes/Public/py/新建文本文档.txt'
text = open(path,'r',encoding='utf-8').read()
#使用结巴的函数对文本进行分词
words = jieba.lcut(text)
#需要排除一些不是人名的单词
excludes = ['将军','却说','二人','不可','荆州','不能','如此','商议','如何'
,'军士','左右','天下','次日','大喜','引兵','军马','东吴','于是'
,'今日','不敢','魏兵','陛下','一人','人马','汉中','不知','只见',
'众将','蜀兵','上马','大叫']
#定义字典类型去存储文字和文字出现的次数
counts = {}
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
elif word == '诸葛亮'or word == '孔明曰':
rword = '孔明'
elif word == '玄德'or word == '玄德曰' or word == '主公':
rword = '刘备'
elif word == '孟德'or word == '丞相':
rword = '曹操'
elif word == '关公'or word == '云长':
rword = '关羽'
elif word == '都督':
rword = '周瑜'
elif word == '后主':
rword = '刘禅'
elif word == '太守':
rword = '刘度'
else:
rword = word
#counts[rword] = counts.get(rword,0) + 1
#把一些不是人名的词语排除掉
for word in excludes:
del counts[word]
items = list(counts.items())
#根据iems的第二个值进行从大到小的排序
items.sort(key = lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)
for i in range(15):
word,count = items[i]
print("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word,count))
#左对齐,占位10位,填充字符为空格
词频统计并生成词云
import jieba
import wordcloud
from imageio import imread
mask = imread("fan.jpeg")
f = open("新建文本文档.txt", "r", encoding = "utf-8")
t = f.read()
f.close()
ls = jieba.lcut(t)
txt = " ".join(ls)
w = wordcloud.WordCloud( font_path= "PingFang.ttc", mask = mask, width = 1000, height = 700, background_color = "white")
w.generate(txt)
w.to_file("threekingdoms.png")
计算个位十位百位
n = int(input("请输入一个三位数"))
a = n // 100
b = n // 10 % 10
c = n % 10
print("百位数、十位数、个位数分别为", a, b, c)
圆的面积
r = 5.1
area = 3.14159 * r * r
print("半径为", r, "的圆的面积是", round(area, 2), sep=" ", end='\n')
print("半径为" + str(r) + "的圆的面积是" + str(round(area, 2)))
print("半径为%.1f的圆的面积是%6.2f" % (r, area))
print("半径为{}的圆的面积是{:6.2f}".format(r, area))
print(f"半径为{r}的圆的面积是{area:6.2f}")
解方程组
mport math
a = float(input("请输入系数a:"))
b = float(input("请输入系数b:"))
c = float(input("请输入系数c:"))
delta = b * b - 4 * a * c
x1 = (-b + math.sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a)
x2 = (-b - math.sqrt(delta)) / (2 * a)
print("方程的两根为", x1, x2)
水仙花数
a=0
b=0
c=0
i=input('第一个三位数')
o=input('第二个两位数')
I=eval(i)
O=eval(o)
for I in range(I,O+1):
a = I // 100
b = I // 10 % 10
c = I % 10
if a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==I:
print(I)
取大于100且被16整除后10位
i = 100
while True:
if i % 15 == 0:
break
i = i + 1
print(i, end=' ')
for j in range(1, 11):
print(j + i, end=' ')
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/取余,输出后10.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py')
105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 '''
奇数合
s=0
z=0
for i in range(101):
z=z+i
if i%2==0:
s=s+i
print(z-s)
分级
score = input('请输入分数:')
sc = int(score)
if sc>=90:
print('A')
elif sc>=80:
print('B')
elif sc>=70:
print('C')
elif sc>=60:
print('D')
else:
print('E')
Person.py
class Person():
'''表示人员的类'''
def __init__(self, name="", age=0):
self.__name = name #私有数据成员
self.age = age
def run(self):
print(" I am running.")
def sayHello(self):
print(" Hi, I am {}, {} years old.".format(self.__name, self.age))
def sing(self, song):
print(" sing a song:", song)
# 实例化对象
li = Person("李明", 18)
wang = Person("王强", 19)
# 使用对象的属性
#print(li.name) #私有数据成员无法直接通过类对象进行访问
print(li._Person__name) #私有数据成员的特殊访问方法
print(li.age)
print(wang.age)
# 调用对象的方法
li.run()
wang.sing("Happy birthday")
li.sayHello()
wang.sayHello()
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2/Person.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2')
李明
18
19
I am running.
sing a song: Happy birthday
Hi, I am 李明, 18 years old.
Hi, I am 王强, 19 years old.'''
Student.py [引用前程序为模块]
from Person import Person
class Student(Person):
'''表示学生的类'''
def __init__(self, name="", age=0, school="", score=0):
super().__init__(name, age)
self.school = school
self.score = score
def isGood(self):
return self.score >= 85
def sayHello(self):
super().sayHello()
print(" I am from " + self.school)
zhang = Student("张芳", 18, "北大", 90)
zhang.run() #继承自Person
#print(zhang.name) #继承自Person
print(zhang.score) #新增的属性
print(zhang.isGood()) #新增的方法
zhang.sayHello() #修改过的方法
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2/Student.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2')
李明
18
19
I am running.
sing a song: Happy birthday
Hi, I am 李明, 18 years old.
Hi, I am 王强, 19 years old.
I am running.
90
True
Hi, I am 张芳, 18 years old.
I am from 北大'''
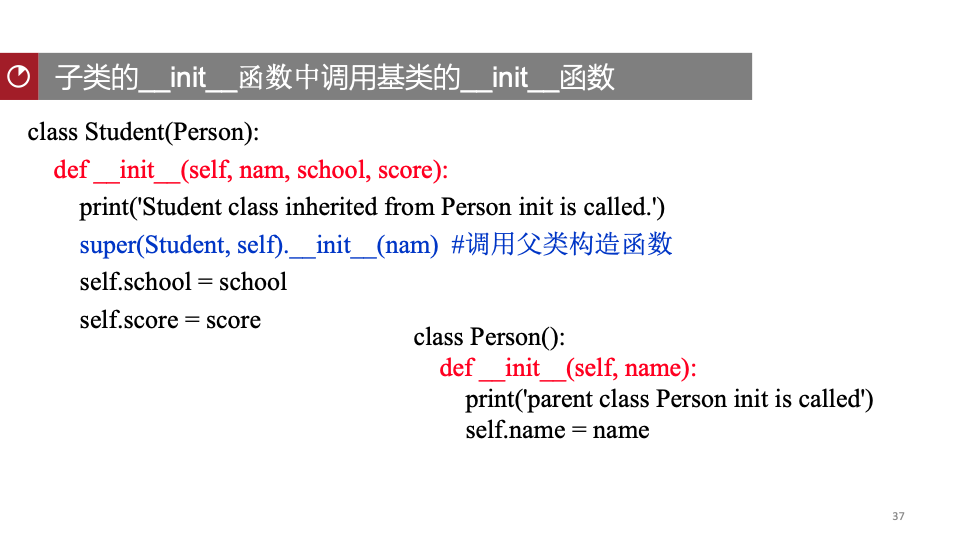
super-attribute-initialization.py
class Person():
def __init__(self, name):
print('parent class Person init is called')
self.name = name
def introduce(self):
print('hello, my name is {}.'.format(self.name))
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self, nam, school, score):
print('Student class inherited from Person init is called.')
super(Student, self).__init__(nam) #调用父类构造函数
self.school = school
self.score = score
def introduce_withoutName(self):
print('hi, i am a student, i come from {} school, and my score is {}.'.format(self.school, self.score))
def introduce(self):
print('hi, i am a student, my name is {}, i come from {} school, and my score is {}.'.format(self.name, self.school, self.score))
stu1 = Student('张三', '北京三中', '99')
stu1.introduce_withoutName()
#stu1.introduce()
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2/super-attribute-initialization.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2')
Student class inherited from Person init is called.
parent class Person init is called
hi, i am a student, i come from 北京三中 school, and my score is 99.'''
staticMethod.py
class Document():
WELCOME_STR = 'Welcome! The context for this book is {}.'
def __init__(self, title, author, context):
print('init function called')
self.title = title
self.author = author
self.__context = context # __ 开头的属性是私有属性
# 静态函数
@staticmethod
def get_welcome(context):
return Document.WELCOME_STR.format(context)
def get_context_length(self):
return len(self.__context)
def intercept_context(self, length):
self.__context = self.__context[:length]
harry_potter_book = Document('Harry Potter', 'J. K. Rowling', '... Forever Do not believ')
print(harry_potter_book.title)
print(Document.WELCOME_STR)
print(harry_potter_book.WELCOME_STR)
print(harry_potter_book.get_context_length())
harry_potter_book.intercept_context(10)
print(harry_potter_book.get_context_length())
print(Document.get_welcome('by class, indeed nothing'))
print(harry_potter_book.get_welcome('by object, indeed nothing'))
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2/staticMethod.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2')
init function called
Harry Potter
Welcome! The context for this book is {}.
Welcome! The context for this book is {}.
25
10
Welcome! The context for this book is by class, indeed nothing.
Welcome! The context for this book is by object, indeed nothing.'''
polymorphism.py
class Person():
def __init__(self, name):
print('parent class Person init is called')
self.name = name
def introduce(self):
print('hello, my name is {}.'.format(self.name))
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self, nam, school):
print('Student class inherited from Person init is called.')
super(Student, self).__init__(nam) #调用父类构造函数
self.school = school
def introduce(self):
print('hi, i am a student, my name is {}, i come from {} school.'.format(self.name, self.school))
class Worker(Person):
def __init__(self, nam, company):
print('Worker class inherited from Person init is called.')
super(Worker, self).__init__(nam) #调用父类构造函数
self.company = company
def introduce(self):
print('hi, i am a worker, my name is {}, i come from {} company.'.format(self.name, self.company))
def selfIntroduce(p):
p.introduce()
stu1 = Student('小明', '北京三中')
worker1 = Worker('张三', '富士康')
selfIntroduce(stu1)
selfIntroduce(worker1)
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2/polymorphism.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2')
Student class inherited from Person init is called.
parent class Person init is called
Worker class inherited from Person init is called.
parent class Person init is called
hi, i am a student, my name is 小明, i come from 北京三中 school.
hi, i am a worker, my name is 张三, i come from 富士康 company.'''
Point_str.py
class Point:
'''表示点的类'''
def __init__(self, x=0, y=0):
'''初始化'''
self.x = x
self.y = y
def __str__(self):
'''转成字符串'''
return "P(%.2f, %.2f)" % (self.x, self.y)
def __add__(self, another):
'''加法'''
return Point(self.x + another.x, self.y + another.y)
def __mul__(self, k):
'''乘法'''
return Point(self.x * k, self.y * k)
# 实例化对象
p = Point(5.1, 0.7)
# 使用其属性
print(p.x, p.y)
# 调用__str__
print(str(p))
# 调用__add__
p3 = p + Point(1,2)
print(p3)
# 调用__mul__
print(p * 2)
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2/Point_str.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2')
5.1 0.7
P(5.10, 0.70)
P(6.10, 2.70)
P(10.20, 1.40)'''
private_attribute.py
class HighSchool_Stuent:
def __init__(self):
self.__name = "张三"
def __Say(self):
# 在类内部使用私有成员变量__name
print("my name is:", self.__name)
boy = HighSchool_Stuent()
# 通过object.s_class__atttribute可以在外部访问私有变量__name
print("name of boy:", boy._HighSchool_Stuent__name)
'''runfile('/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2/private_attribute.py', wdir='/Volumes/Public/py/6-class 2')
name of boy: 张三'''
分数查询
inFile = open("score.txt", "r", encoding="GBK")
key = input("要查找的姓名或学号?")
inFile.readline() #读取并忽略标题行
for line in inFile.readlines():
if line == "":
continue #忽略空行
values = line.rstrip('\n').split("\t") #注意split的使用
#print(values)
s_id = values[0]
s_name = values[1]
if key in s_id or key in s_name: # 模糊查找
print('学号', s_id, '姓名', s_name)
print("各次成绩:", values[2:])
inFile.close()
添加行号
'''给文件加上行号'''
fileName1 = "file_read_seek.py"
fileName2 = "file_read_seek.txt"
f1 = open(fileName1, "r", encoding="utf-8")
f2 = open(fileName2, "w", encoding="utf-8")
n = 1 #行号变量
for line in f1.readlines():
if "#" in line:
line = line[0: line.find("#")].rstrip() + "\n" #去掉#后面的文字
s = str(n) + ":\t" + line #加上行号及制表符
f2.write(s)
n += 1
f1.close()
f2.close()
图片复制
import os
listdir = os.listdir() #无参数默认为当前路径
cPath = os.getcwd()
print(cPath)
print('sea.jpg图片文件的大小为:{}'.format(os.path.getsize('sea.jpg')))
==========================================================================================================